Brass Rod: A Poster Child for Sustainability
Brass rods, made from an alloy of copper and zinc, stand as indispensable materials renowned for their machinability, versatility, strength, and durability. Their significance spans a diverse range of industries, finding applications in electronics, plumbing, automotive parts, industrial machinery, construction, and beyond.
Brass rods boast impressive versatility, available in round, hexagonal, and square shapes. They excel in environments demanding resistance to corrosion, wear, high temperatures, and pressures. As we examine brass further, we'll explore how its production and use contribute to a circular economy, lessen environmental impact, and encourage economic growth.
Market Growth Driven by Sustainability
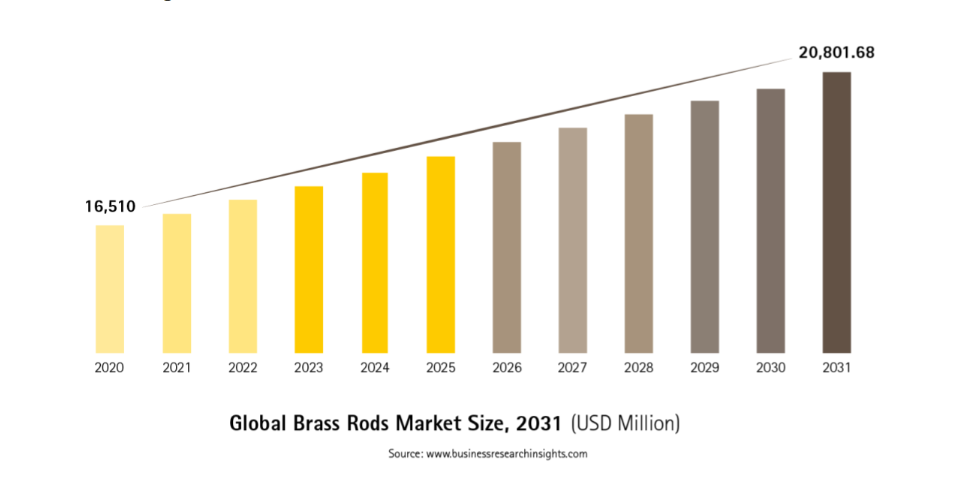
The brass rod market size is projected to reach USD 20.80 million by 2031, driven in part by the increase in construction activities and use in electrical components with both of these industries pursing environmental consciousness. Manufacturers are prioritizing sustainable practices, and brass rod's inherent recyclability and low carbon footprint are fueling its demand.
Brass Rod: A Champion of Recycling
One of the most compelling benefits of brass rod is its ability to be recycled an infinite number of times without any loss of chemical or physical properties – when re-melted and formed back into its raw state, it retains the exact same properties as the starting material. Brass is one of the most recycled metals globally. In fact, many brass product lines feature over 95% recycled content.
Recycling brass significantly reduces the need for virgin materials (copper and zinc), lessens environmental impact, and keeps waste out of landfills. It's a vital component of the circular economy, where resources are reused rather than discarded after single use.
The production economics of brass rod are built upon a "closed loop" recycling process. In this system, brass scrap generated during subtractive manufacturing processes (e.g., machining and forging to produce finished parts) is returned back to the producing rod mills where it is directly remelted, cast, and extruded back into new brass rod products. Brass scrap containing different alloying elements is segregated by manufactures to avoid contamination issues during the recycling process. This strict separation ensures the quality and reusability of the recycled brass, cycle after cycle. Collaborative efforts among rod mills, machine shops, and scrap yards to keep different alloy streams separate is essential to ensure the long-term viability of brass recycling.
Economic and Environmental Advantages of a Circular Brass Rod Industry
Brass rod production boasts several environmental advantages beyond its recyclability. Here are some key points:
- Reduced Energy Consumption: Brass rod requires significantly less energy to machine compared to other metals like steel. This translates to lower operational carbon emissions and a smaller environmental footprint.
- Reduced Landfill Waste: By maximizing recycling, brass rod helps divert waste from landfills, promoting a more sustainable waste management system.
The environmental benefits of brass rod are coupled with economic advantages:
- Brass is a champion of resource efficiency. Because this valuable non-ferrous metal is incredibly durable and lasts for years, coupled with its endless recyclability, the need for virgin resources is significantly reduced. Unsurprisingly, recycling brass is far more cost-effective than using primary materials. The lower energy consumption involved in recycling translates directly to cost savings.
- A catalyst for job creation: The global recycling industry is experiencing tremendous growth, and this translates to significant job creation. According to the 2020 Recycling Economic Information (REI) Report, the industry generated a substantial 681,000 jobs and USD 5.5 billion in tax revenue. While this report doesn't distinguish between specific recycling operations or material flows, it undeniably highlights recycling's power to drive employment opportunities. This job creation is crucial for fostering a thriving and sustainable local economy. More jobs translate to increased income for residents, which in turn fuels consumer spending and economic growth. A robust recycling sector empowers communities by creating a cycle of economic and environmental well-being. As more jobs are created in the recycling industry, residents have a greater financial stake in the success of these initiatives, further propelling environmentally conscious practices.
- High Residual Value: Brass stands out for its high residual value compared to other scrap metals, making it an attractive option for both businesses and individuals. Brass rod itself is made from a very high percentage of recycled content, keeping costs down from the get-go. But the real advantage lies in its end-of-life value. Unlike many materials, brass scrap retains an impressive 75-85% or more of its original value. This translates to significant cost savings for manufacturers who can sell their brass scrap to local recyclers or directly to rod mills, gaining greater control over their raw material costs.
Brass rod's exceptional combination of recyclability, lower energy consumption, and economic viability makes it a shining example of sustainability within the circular economy. It offers a compelling solution for manufacturers and consumers seeking to reduce their environmental footprint. By choosing brass rod, we can collectively contribute to a greener future with minimized environmental impact and a thriving circular economy. This responsible choice not only benefits the environment, but also fosters economic prosperity through job creation and resource efficiency.
